In the ever-evolving realm of electrical engineering, the role of "Ct On Transformer" is gaining significant attention due to its numerous benefits and applications. Industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned authority in power systems, states, "The implementation of current transformers can significantly enhance the reliability and safety of electrical networks." This insightful observation underscores the critical importance of understanding and utilizing Ct On Transformer technology in both industrial and commercial sectors.
Current transformers (CTs) are essential components that facilitate precise measurement and monitoring of electrical currents, ensuring that power systems operate efficiently and safely. As the demand for energy continues to rise, the integration of Ct On Transformer within various applications not only improves operational efficiency but also promotes the advancement of smart grid technologies. This introduction aims to illuminate the fundamental aspects of Ct On Transformer, exploring its key benefits, operational principles, and the diverse applications that make it indispensable in modern electrical frameworks. By delving into these elements, we can appreciate the substantial impact of Ct On Transformer on the future of energy management and system performance.

Current transformers (CTs) are essential components in electrical engineering, designed to measure alternating current (AC) while isolating high-voltage circuits from measuring instruments. By transforming high current to a lower, proportional value, CTs provide safety and efficiency in monitoring electrical systems. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), CTs can accurately measure currents ranging from a few milliamperes to several thousand amperes, making them vital for power system management.
The functionality of CTs extends beyond just measurement; they play a crucial role in protection and control systems. They enable relay systems to detect fault conditions and ensure that circuit breakers operate effectively to prevent damage to electrical equipment. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the current transformer market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 8% from 2021 to 2026, driven by the increasing demand for grid modernization and the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid. This trend highlights the importance of CTs in facilitating the transition to smarter and more reliable energy systems, thereby underscoring their value in various industrial applications.
| Dimension | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Current transformers provide precise measurements of electrical currents. | Enhanced measurement accuracy leading to better system monitoring. | Used in metering and protective relaying systems. |
| Safety | Isolate high-voltage circuits while measuring current. | Increased safety for personnel and equipment. | Integral in substation automation and protection systems. |
| Versatility | Can be used with different types of electrical systems. | Flexibility in application across various industries. | Applicable in power generation, transmission, and distribution. |
| Cost-effective | Relatively low-cost solution for current measurement. | Lower installation and maintenance costs compared to other methods. | Widely used in commercial and industrial applications. |
Current transformers (CTs) serve a crucial role in power monitoring and protection systems within electrical grids. By accurately converting high currents into manageable values, CTs enable measurement, monitoring, and control without direct exposure to dangerous levels of electricity. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global current transformer market is expected to grow from $2.6 billion in 2021 to $3.8 billion by 2026, highlighting the rising importance of these devices in enhancing electrical safety and reliability.
One of the key benefits of current transformers is their ability to provide precise current measurements essential for electrical protection schemes. They facilitate the operation of protective relays which can detect abnormalities in electrical currents, such as overloads or short circuits, effectively averting potential equipment damage or catastrophic failures. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) states that effective current measurement within power systems is fundamental to maintaining coordination among protective devices, thereby reducing downtime and associated costs for utility companies.
In addition to operational safety, CTs contribute significantly to energy efficiency. By enabling real-time monitoring of electrical consumption, they empower organizations to identify inefficiencies and implement corrective measures. According to a study by the U.S. Department of Energy, industrial facilities that utilize advanced monitoring systems can achieve energy savings of 10-20%. This level of insight not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with global sustainability goals, making current transformers an indispensable component in modern electrical infrastructure.
This bar chart represents the key benefits of current transformers in power monitoring. Each benefit is rated based on a percentage scale, indicating how vital they are in enhancing efficiency and safety in electrical systems.
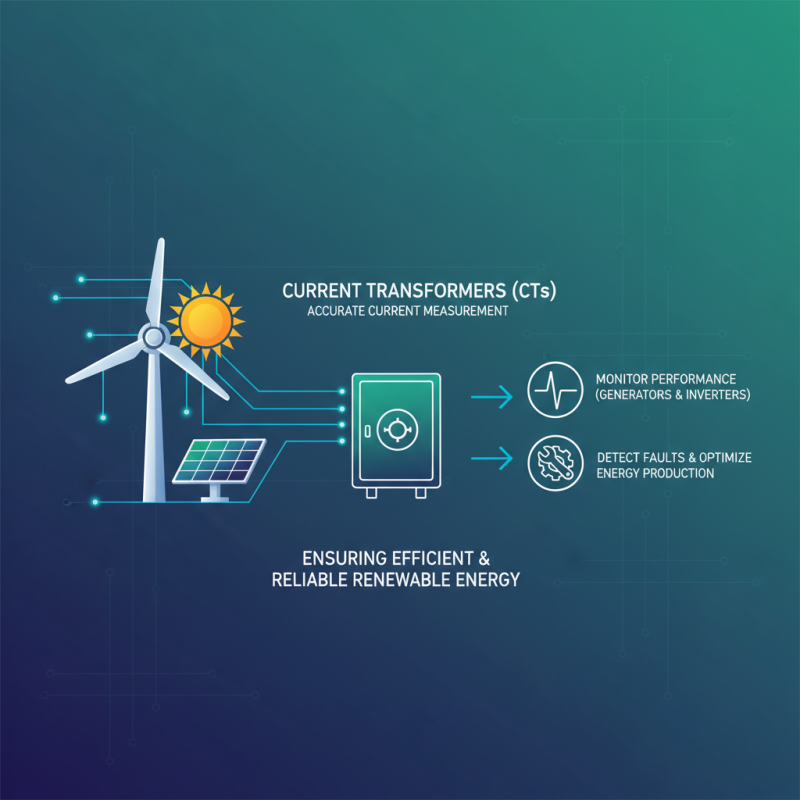
Current transformers (CTs) play a vital role in renewable energy systems by providing accurate measurement of electrical current, ensuring efficient energy management. In wind and solar power installations, CTs are utilized to monitor the performance of generators and inverters, which is crucial for optimizing energy production and maintaining system stability. By leveraging CTs, operators can detect fluctuations in current that might indicate issues such as equipment malfunction or underperformance, enabling timely interventions before minor issues escalate into significant operational problems.
Moreover, CTs are essential for integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. They facilitate the monitoring of power flow, helping to balance supply and demand in real-time. For instance, during peak generation periods from solar or wind sources, CTs assist in quantifying the output, thus allowing grid operators to adjust settings for stability. Additionally, these transformers are instrumental in implementing energy management systems that harness data for improved efficiency and reduced losses in transmission. This capability is particularly beneficial as the reliance on renewables continues to grow, making CTs indispensable in modern energy infrastructures.
Current transformers (CTs) and voltage transformers (VTs) are pivotal components in electrical systems, each serving distinct purposes and applications.
A current transformer is primarily designed to measure alternating current (AC) flow in a conductor. By providing a scaled-down representation of the current, CTs ensure safety and accuracy in monitoring large electrical currents. This capability is critical for protective relaying and metering in high-voltage applications, where direct measurement would be impractical and dangerous.
In contrast, voltage transformers are utilized to measure voltage levels, offering insights into the electrical potential within a system. VTs step down high voltages to safer levels suitable for instrumentation and metering purposes. This is essential for ensuring accurate voltage measurements, which are crucial for system stability and protection mechanisms.
While both transformers serve measurement needs, the primary distinction lies in their output: CTs convert current into a manageable output proportional to the input current, while VTs transform voltage levels to facilitate safe monitoring and control. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the appropriate transformer type based on specific application requirements and safety considerations.
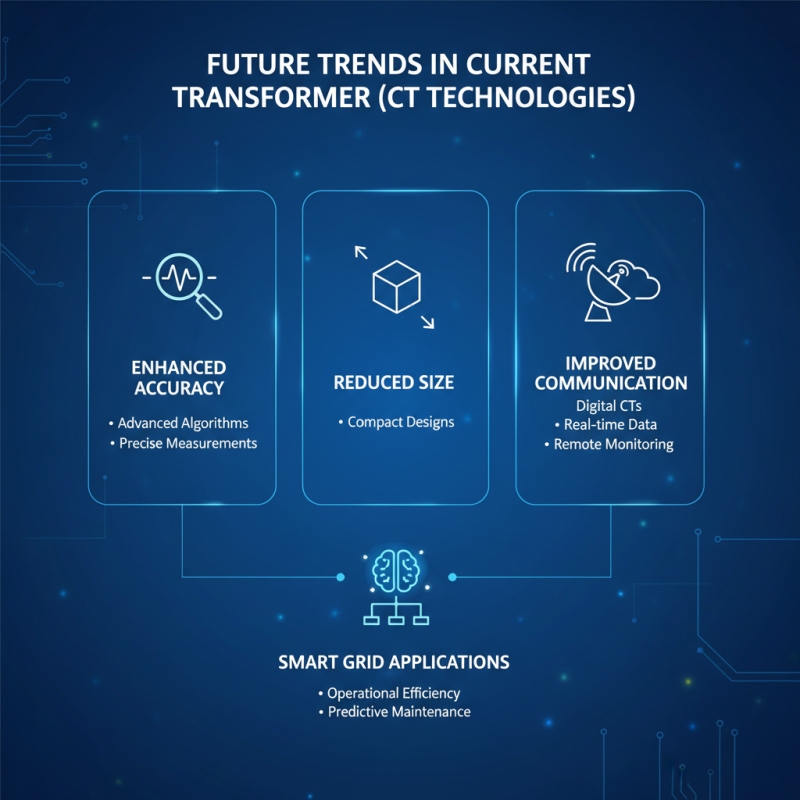
As the demand for efficient energy management grows, innovations in current transformer (CT) technologies are becoming increasingly essential. Future trends in CTs focus on enhancing accuracy, reducing size, and improving communication capabilities. Digital CTs, which utilize advanced algorithms and digital signal processing, are gaining traction, offering precise measurements and the ability to transmit data in real-time. This technology not only boosts operational efficiency but also enables smart grid applications, opening avenues for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Tips: When considering the implementation of digital CTs, assess the compatibility with existing infrastructure and the potential for scalability. Invest in training for personnel to effectively understand and leverage the new technologies, maximizing their benefits.
Another exciting trend is the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) into current transformers. With IoT-enabled CTs, utilities can collect and analyze vast amounts of data for better decision-making. This integration facilitates enhanced grid reliability and helps in fault detection, reducing downtime. Additionally, as sustainability becomes a priority, the development of eco-friendly CT materials and designs is on the rise, aligning with global efforts to minimize environmental impact.
Tips: Keep an eye on emerging standards and protocols for IoT devices in the energy sector. Staying updated will help integrate new technologies seamlessly and ensure compliance with industry regulations.