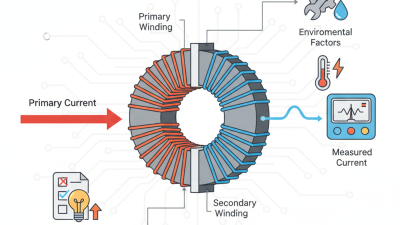
In the realm of electrical engineering, the Silicon Steel Transformer Core plays a pivotal role. This core is essential in transformers, enhancing efficiency and reducing energy losses. Understanding the various types of silicon steel transformer cores is crucial for optimizing performance.
Different designs exist, each catering to specific applications. Some cores favor high efficiency, while others prioritize cost-effectiveness. The choice often reflects a balance between performance and budget. However, this balance isn't always straightforward. It's vital to weigh the pros and cons of each type, considering factors like magnetic properties and manufacturing techniques.
As we explore the top types of silicon steel transformer cores, we uncover both innovation and limitations. Each core type has its strengths and weaknesses, often leading to debate among engineers. This journey through silicon steel transformer cores is not merely technical; it involves thoughtful consideration of choices and impacts in the electrical landscape.

Silicon steel is critical in transformer cores, significantly impacting efficiency. It is designed to reduce energy loss during operation. The most common types include grain-oriented and non-grain-oriented silicon steel. Grain-oriented steel provides high magnetic permeability. This leads to lower losses in high-frequency transformers. Reports indicate that steel with 3% silicon content is widely used, offering up to 30% more efficiency.
Non-grain-oriented silicon steel, on the other hand, is versatile and used in various types of transformers. It excels in applications where directionality is less critical. However, its magnetic properties can vary widely. A study showed that using higher silicon content in non-grain-oriented types tends to increase performance but adds to manufacturing complexity. Not all producers achieve the ideal balance, which can lead to performance inconsistencies.
Despite advancements, challenges persist. Many manufacturers struggle with maintaining uniform quality across batches. Variations in alloying elements can affect magnetic properties. As these types of steel evolve, ongoing research focuses on enhancing efficiency while reducing costs. The industry must address these issues to meet rising demands for energy-efficient transformers.
Silicon steel is essential for transformer cores. It greatly influences transformer efficiency. Its magnetic permeability is key. This property allows for better magnetic flux flow. Higher permeability means less energy loss. This translates to improved performance for transformers.
Choosing the right silicon steel type is critical. Different grades have varying levels of silicon content. More silicon generally means better performance. However, higher silicon also increases brittleness. Balancing these properties can be tricky. A core that is too brittle may not withstand operational stresses. Users must weigh the trade-offs.
**Tips:** Check specifications carefully. Understand the applications for various grades. Consider the environment where the transformer will operate. Not all silicon steels suit every application, and mismatched types can lead to inefficiency. Be mindful of your choices.
| Type of Silicon Steel | Electrical Resistivity (μΩ·m) | Core Loss (W/kg) | Magnetic Flux Density (T) | Thickness (mm) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel | 0.4 - 0.6 | 1.0 - 1.5 | 1.8 - 2.2 | 0.3 - 0.5 | Power Transformers |
| Non-oriented Silicon Steel | 0.5 - 0.7 | 1.5 - 2.0 | 1.6 - 1.9 | 0.5 - 0.7 | Distribution Transformers |
| Amorphous Steel | 0.2 - 0.4 | 0.5 - 0.8 | 1.5 - 1.8 | 0.3 - 0.4 | Eco-friendly Transformers |
When discussing silicon steel transformer cores, the choice between grain-oriented and non-grain-oriented types is crucial.
Grain-oriented silicon steel is engineered for maximum efficiency. It features a specific grain direction that reduces energy losses during magnetic flux. This orientation results in lower hysteresis losses and improved overall performance. However, the production process is complex and often more expensive.
In contrast, non-grain-oriented silicon steel offers flexibility. It performs well in a variety of applications but lacks the efficiency of its grain-oriented counterpart. It can be used in situations where precision is less critical. This might lead to a trade-off in energy efficiency and performance. Some users appreciate its cost advantages, while others desire the efficiency gains from grain-oriented options.
In essence, the choice depends on the application requirements. Users often wrestle with the decision. The bottom line is specific applications may benefit from either type. Knowing the differences helps in making a more informed choice. Each type has its pros and cons, reflecting the ongoing debate in the industry.

The demand for silicon steel transformer cores is projected to rise significantly by 2026. Factors such as growing energy needs and advancements in electrical infrastructure play a crucial role. The global market is expected to reach approximately $5 billion, driven by increased production and consumption of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources.
The continuous focus on efficiency is reshaping the industry. Companies are investing in advanced manufacturing techniques to enhance core performance. For instance, thinner silicon steel sheets are becoming the norm. These sheets reduce energy loss, making transformers more efficient. Yet, challenges remain. Material costs fluctuate, impacting profits. Additionally, the recycling of silicon steel needs more attention. A sustainable approach could protect the environment while meeting demand.
Emerging economies contribute significantly to market growth. In India and China, rapid urbanization spikes energy demand. As a result, local manufacturers are ramping up production. They face intense competition from global players. Prices may stabilize, but overcapacity is a risk. Analysts warn that manufacturers must innovate continually to remain competitive. Balancing technology and cost is vital in navigating this evolving landscape.
The advancements in silicon steel technology for transformers have significantly enhanced efficiency in electrical systems. Recent innovations focus on improving magnetic properties. This development leads to higher performance and reduced energy losses. New manufacturing techniques are emerging, optimizing the grain alignment in silicon steel. Such techniques promise better conductivity and strength, contributing to overall transformer reliability.
Tips: When selecting transformer cores, consider the specific application. Not all steel types fit every transformer. Research the performance characteristics. Look for data that confirm efficiency improvements.
Another noteworthy trend involves the use of thinner laminations. Thinner laminations help in reducing eddy current losses. However, they may pose manufacturing challenges. Achieving uniform thickness remains a goal. Manufacturers should focus on refining processes to create consistent quality.
Tips: Investigate the thickness of materials. Sometimes thinner is better, but not always. Your project's requirements dictate the choice. Balancing cost and performance is crucial for optimal results.