Choosing the right Distribution Transformer Core is crucial for optimal performance in electrical systems. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, the demand for efficient transformers has surged by 15% since 2020. This shift emphasizes the need for industry professionals to focus on core selection. The core affects efficiency, losses, and overall reliability.
When selecting a Distribution Transformer Core, you must consider materials, construction, and design. Standard options include silicon steel and amorphous steel. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. For instance, silicon steel is common but has higher losses compared to amorphous steel. Such choices can significantly impact operational costs over time.
It's easy to overlook details during the selection process. Some industries prioritize cost over quality, leading to future inefficiencies. A subpar core can result in increased energy losses, affecting the bottom line. Reflecting on these factors can lead to better long-term decisions. Investing in the right Distribution Transformer Core is not just about immediate requirements; it’s about future-proofing your electrical infrastructure.
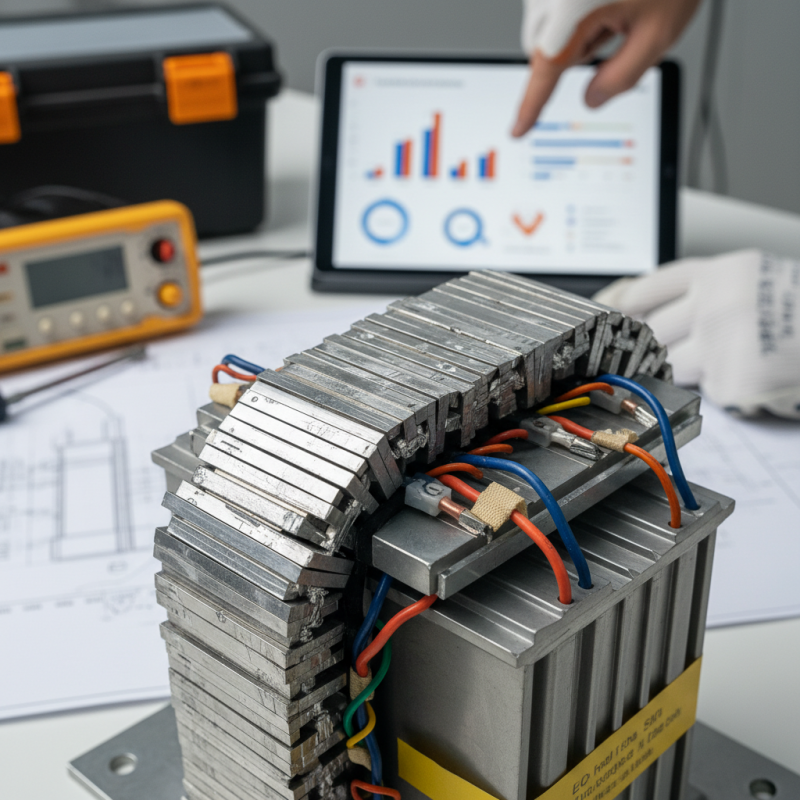

Distribution transformer cores play a crucial role in energy efficiency and voltage regulation. They directly influence the performance of transformers. Selecting the right core material can greatly affect the overall losses in the unit. Core materials such as silicon steel and amorphous steel have significant differences. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks in terms of cost, efficiency, and size.
The shape of the core also matters. Common shapes include E, C, and toroidal styles. E-shaped cores are popular for their easy assembly. However, they may not always provide optimal efficiency. Toroidal cores, while efficient, can be more complex to manufacture. It’s essential to weigh these factors against your operational needs.
Even with the right materials and shapes, real-world conditions can create inefficiencies. Temperature fluctuations and mechanical stresses can impact a core's performance. Users should regularly inspect and maintain their transformers to avoid unexpected issues. While there are guidelines available, they don’t cover every scenario. Flexibility and understanding of specific needs are key. Choosing the right distribution transformer core requires careful consideration and reflection on operational goals.
| Core Material | Magnetic Flux Density (Tesla) | Efficiency (%) | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | 1.5 | 95 | 300 |
| Amorphous Steel | 1.45 | 98 | 500 |
| Ferrite Core | 0.8 | 90 | 200 |
| Copper Core | 1.7 | 97 | 800 |
Choosing the right materials for a distribution transformer core is crucial. The core directly impacts efficiency and performance. Common materials include silicon steel and amorphous steel. Silicon steel is known for reducing energy losses. A report from the Electric Power Research Institute highlights that using silicon steel can lower losses by 30%. However, it is heavier and may increase transportation costs.
Amorphous steel, on the other hand, offers better energy efficiency. Its unique properties lead to lower core losses. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory shows that amorphous cores can provide up to 70% lower losses compared to traditional silicon cores. This material, however, can be more expensive and may not suit every project budget.
While both options have benefits, it's vital to consider specific project requirements. A heavy core might hinder installation. Additionally, the cost-performance ratio must be carefully analyzed. Selecting the right material could mean significant savings over time, but it requires thorough research and understanding of each material's trade-offs. Don't overlook the importance of core design and its role in optimizing performance.
This chart illustrates the composition of materials typically used in the construction of distribution transformer cores. Silicon steel is the most commonly used material, followed by amorphous steel, copper, and aluminum.

When selecting a distribution transformer core, several critical factors come into play. Magnetic properties are paramount. Materials like silicon steel have low core losses. However, some users may overlook efficiency ratings. Higher efficiency often translates to better performance and reduced energy costs.
Size and weight also matter. A well-chosen core isn't just about specifications. It should fit the installation area. A bulky core may lead to unnecessary struggles during installation. Environmental conditions should not be ignored. Humidity and temperature can influence core performance significantly.
Budget is another reality. Choosing a cheaper core can sometimes lead to long-term inefficiencies. Striking a balance between cost and quality is essential. Not every option brings the best long-term value. Consistent reevaluation of choices is crucial. This means reflecting on past decisions and learning from previous experiences. Selecting the right core requires careful consideration of these diverse factors.
Choosing the right transformer core is crucial for optimal performance. The core material directly impacts efficiency. Common choices include silicon steel and amorphous steel. Each has unique properties that can affect the transformer's losses. Silicon steel is prevalent due to its availability and proven performance. Amorphous steel offers lower core losses but may have limitations in other areas.
Evaluating the efficiency involves understanding magnetic properties. The hysteresis curve of the core material indicates how well it can handle magnetic flux. A more efficient core undergoes less energy loss. Consider the frequency of operation as well. Higher frequencies can amplify losses in certain materials. Real-world scenarios often reveal performance gaps, prompting the need for detailed analysis.
Manufacturers sometimes overlook the long-term implications of core choice. It’s not just about immediate efficiency. Operational conditions can change. This inconsistency can lead to unexpected failures and high maintenance costs. Emphasizing core material testing under various conditions will help in identifying the best options. Investing time in this evaluation reduces risks associated with transformer performance.
When it comes to choosing a distribution transformer core, installation and maintenance are critical aspects. A well-installed core can enhance the efficiency of the transformer significantly. Incorrect installation could result in overheating. According to industry reports, improper installation causes over 30% of transformer failures.
Regular maintenance is equally important for transformer cores. Monitor the core for signs of wear or overheating. Inspections should occur at least once a year, focusing on joints and connections. A study by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers stated that 25% of transformers fail due to inadequate maintenance.
While many manufacturers provide guides, not all cores are the same. Each environment presents unique challenges. Sometimes, insufficient training in maintenance practices leads to oversights. In that case, a well-documented maintenance schedule is essential. This ensures every team member follows best practices and can identify potential issues early on.