The advent of Hall magnetic sensors has revolutionized the fields of positioning and motion detection, providing solutions that enhance both accuracy and reliability. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global magnetic sensors market is projected to reach $6.2 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2020 to 2025. This growth is largely driven by the increasing demand for advanced sensing technologies in various applications, including automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial automation.
Hall magnetic sensors operate based on the principle of the Hall effect, which enables the detection of magnetic fields and the precise measurement of position and motion. Their efficiency in different environmental conditions, combined with their compact size and low power consumption, makes them ideal for various applications, such as proximity sensing, angle measurement, and speed detection. As industries strive for greater automation and precision, the integration of Hall magnetic sensors into systems becomes increasingly critical to achieving accurate and real-time data processing.
In an era where smart technologies and IoT devices dominate, the implementation of Hall magnetic sensors is set to play a pivotal role in enabling seamless interaction between devices and their environments. With their potential to enhance performance and operational efficiency, Hall magnetic sensors are poised to become a cornerstone in the future of positioning and motion detection technologies.

Hall magnetic sensors leverage the Hall effect, which is the generation of voltage across a conductor when it is exposed to a magnetic field, to provide precise positional and motion detection capabilities. These sensors operate based on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents, allowing them to detect minor changes in position with high accuracy. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for Hall effect sensors is projected to reach USD 4.6 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2020 to 2025. This growth emphasizes the increasing demand for sensors in various applications, including automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial automation.
The functionality of Hall magnetic sensors extends to various positioning applications, such as determining the rotation angle of motors and detecting the proximity of moving objects. For instance, in automotive systems, Hall sensors play a crucial role in enhancing safety features, as they can provide real-time feedback for anti-lock braking systems and electric steering. Furthermore, their robust nature and ability to function in challenging environments make them ideal for industrial settings, where reliability is paramount. A report by Grand View Research indicates that the automotive segment alone accounted for over 30% of the Hall effect sensors market share in 2020, demonstrating their critical role in modern technology ecosystems.
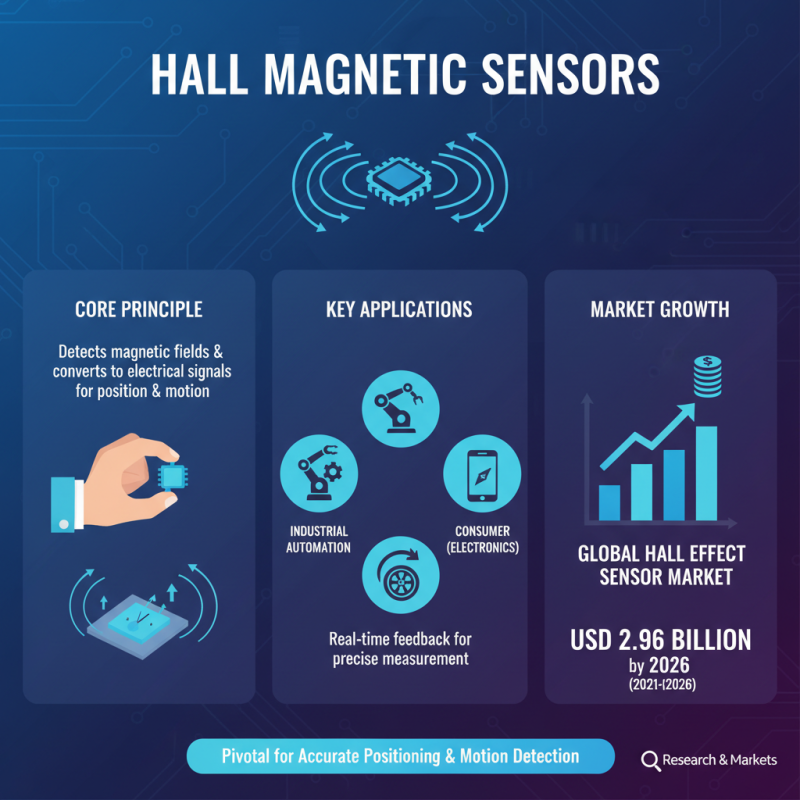
Hall magnetic sensors have become a pivotal technology in the realm of accurate positioning and motion detection due to their unique operating principles. These sensors detect magnetic fields and translate them into electrical signals, allowing for precise measurements of position and movement. The ability of Hall sensors to deliver real-time feedback makes them an essential component in various applications, from industrial automation to consumer electronics. According to a recent market report by Research and Markets, the global Hall Effect sensor market is expected to reach USD 2.96 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.6% from 2021, underscoring the increasing reliance on this technology for precise motion detection.
The fundamental principle behind Hall sensors relies on the Hall effect, which occurs when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the flow of current in a conductive material. As the magnetic field interacts with the charge carriers, it creates a voltage difference, which can be measured and interpreted as a position or movement signal. This principle enables Hall sensors to provide high accuracy and reliability, with positioning error rates as low as ±0.1mm in various applications. Additionally, their robustness against environmental factors like temperature fluctuations and vibration enhances their utility in dynamic situations, making them ideal for use in robotics, automotive applications, and smart devices. With advances in technology, the integration of Hall sensors with advanced algorithms has further improved their performance in motion detection, leading to smarter, more responsive systems across multiple industries.
Hall magnetic sensors have become integral to various applications that demand precise positioning and motion detection. Their ability to sense changes in magnetic fields makes them particularly useful in positioning systems, ranging from robotics to automotive applications. According to a recent industry report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global market for Hall effect sensors is expected to reach approximately $3.2 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for accurate measurement technologies across various sectors.
In positioning systems, Hall sensors provide accurate feedback on the position of moving parts, enabling efficient automation and control. For example, in robotics, Hall sensors can be used to determine the position of motors accurately, allowing for precise movements and enhanced operational efficiency. Furthermore, in automotive applications, they aid in determining the position of components such as throttle and gear position sensors, facilitating smoother transitions and improved vehicle responsiveness. A study by MarketsandMarkets indicated that Hall sensors are expected to have a significant impact on the automotive market, driven by the rising demand for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles.
The integration of Hall sensors in accurate positioning applications is revolutionizing industries by enabling high-resolution tracking and robust detection capabilities. As technology advances, these sensors are expected to become even more refined, directly contributing to the efficiency and reliability of precision systems. The continued investment in developing Hall sensor technology promises to strengthen their position as a cornerstone in modern engineering solutions.
| Application | Sensor Type | Sensitivity (mV/G) | Operating Voltage (V) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Arm Positioning | Linear Hall Sensor | 10 | 5 | Position feedback in robotics |
| Wheel Speed Detection | Digital Hall Effect Sensor | 5 | 12 | Speed monitoring in vehicles |
| Tilt Detection | Analog Hall Sensor | 15 | 3.3 | Tilt sensing in portable devices |
| Linear Position Measurement | LATCH Hall Sensor | 12 | 10 | Measuring displacement in linear actuators |
| Proximity Sensing | Omni-directional Hall Sensor | 8 | 5 | Object detection in automation |
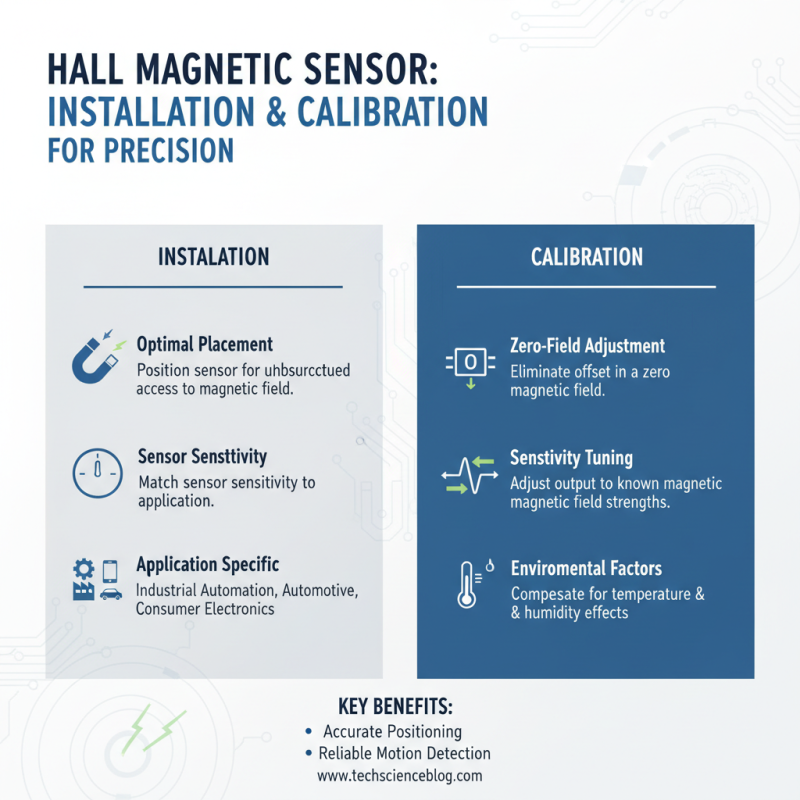
The installation and calibration of Hall magnetic sensors are crucial steps in achieving precise positioning and motion detection in various applications. These sensors operate based on the Hall effect, which allows them to detect the presence and strength of magnetic fields. To ensure optimal performance, it is essential to install the sensors in locations that allow for unobstructed access to the magnetic field being measured. This positioning should account for the sensor's sensitivity and intended application, whether in industrial automation, automotive systems, or consumer electronics.
Calibration is an equally critical process, as it ensures that the sensor output corresponds accurately to the external magnetic field strength. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the demand for Hall effect sensors is projected to increase from USD 1.77 billion in 2020 to USD 2.69 billion by 2025, indicating a growing reliance on their accuracy in positioning systems. Calibration typically involves comparing the sensor output against known reference values and making necessary adjustments. It is recommended to perform this calibration regularly, especially in environments where temperature variations may affect sensor accuracy, thus enabling reliable data collection and enhanced system performance.
When working with Hall magnetic sensors for positioning and motion detection, issues can arise that may hinder their functionality. One common problem is the interference caused by external magnetic fields. This can lead to inaccurate readings or erratic behavior of the sensor. To troubleshoot this, it is essential to examine the sensor’s operating environment and ensure that it is shielded from nearby magnetic sources. Additionally, using appropriate shielding materials can help mitigate any interference, allowing the sensor to function more accurately.
Another frequent issue involves the calibration of the Hall sensors. Improper calibration can result in significant errors in position detection and motion sensing. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for calibration procedures, but also to validate the sensor's performance in real-world applications. If discrepancies are found, re-evaluating the calibration procedure and adjusting the sensor's threshold levels can often resolve the discrepancies. Regular testing and recalibration will ensure that the Hall sensor maintains its accuracy over time, providing reliable performance in various applications.
