In the evolving landscape of electronics engineering, the selection of components plays a critical role in the success of projects, particularly when it comes to managing power levels efficiently. One crucial element that often dictates the reliability and performance of electronic designs is the High Power Switch. According to a recent market analysis by Grand View Research, the global market for high power switching devices is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand for power management in various applications, including renewable energy systems and electric vehicles. Accurate selection and implementation of these switches can enhance system performance and significantly reduce energy losses.
Additionally, a study by Research and Markets highlights that as the demand for energy-efficient solutions rises, the need for sophisticated high power switches that accommodate varying loads and control requirements becomes imperative. These switches must be evaluated based on several criteria, including current and voltage ratings, thermal performance, and switching frequency. Understanding these parameters is essential for engineers and hobbyists alike to navigate their electronic projects successfully. This article aims to provide insights into how to choose the right High Power Switch, ensuring optimal performance and safety in your electronics projects.
High power switches are crucial components in electronics projects that require the handling of substantial electrical currents. Understanding the different types and specifications of high power switches is essential for selecting the right component for your application. The most common types include
mechanical switches,
solid-state relays, and
MOSFETs, each providing unique advantages such as faster switching times, energy efficiency, and durability.
 Mechanical switches are reliable but may not support high switching frequencies, whereas solid-state solutions offer silent operation and longer lifespan, making them suitable for varied applications.
Mechanical switches are reliable but may not support high switching frequencies, whereas solid-state solutions offer silent operation and longer lifespan, making them suitable for varied applications.
When choosing a high power switch, pay close attention to the specifications, including voltage and current ratings, switching speed, and thermal management characteristics. It’s vital that the chosen switch can handle the maximum load of your project without overheating or failing. Additionally, consider the switch's ON resistance, as lower resistance can lead to less power loss during operation, translating to greater efficiency.
Tips for selecting high power switches include:
When selecting high power switches for your electronics project, there are several key factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and safety. One of the primary considerations is the current and voltage ratings of the switch. It is crucial to choose a switch that can handle the maximum current and voltage that your application will encounter. Exceeding these ratings can lead to overheating, component failure, or even dangerous situations. Additionally, it’s important to understand the type of load—whether it is resistive, inductive, or capacitive—as this can affect the switch's durability and operational characteristics.
Another significant factor is the switch's design and interface. Depending on your project's requirements, you might need a specific physical configuration, such as a toggle, push-button, or rotary switch. Furthermore, the ease of integration into your existing circuitry should be evaluated. Consider the connections and the potential need for additional components such as relays or protection devices. Lastly, the switch's durability, including its ability to withstand repeated use and environmental factors like temperature and humidity, will significantly influence the reliability and longevity of your project. Selecting a switch that meets these criteria will help ensure the success of your electronics endeavor.
When selecting a high power switch for your electronics project, understanding the current and voltage ratings is crucial. These specifications dictate how much power the switch can handle without overheating or failing. A switch's current rating, which is typically measured in amperes (A), indicates the maximum amount of current that can safely flow through the switch. Exceeding this rating can lead to catastrophic failure, including arcing and fire hazards. Conversely, the voltage rating reflects the maximum voltage that can be applied across the switch without causing breakdown or insulation failure.
Tips for evaluating these ratings include ensuring that the ratings match or exceed the needs of your application. For instance, if your project operates at 10A and 120V, it's wise to choose a switch rated for at least 20A and 150V to provide a safety margin. Additionally, consider the switching frequency; some switches are optimized for low-frequency applications, while others can handle high-frequency operations with ease.
It’s also advisable to account for environmental factors such as temperature and humidity since these can affect the performance and reliability of the switch. High ambient temperatures can reduce the current rating, so design your project with these conditions in mind. Always check the datasheet of any potential switch for detailed specifications and recommendations to ensure it fits your project's requirements.
| Switch Type | Voltage Rating (V) | Current Rating (A) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOSFET | 60 | 30 | Power Regulation |
| IGBT | 1200 | 50 | Motor Control |
| Relay | 250 | 20 | Load Switching |
| Triac | 600 | 16 | AC Control |
| Solid State Relay | 480 | 40 | Industrial Automation |
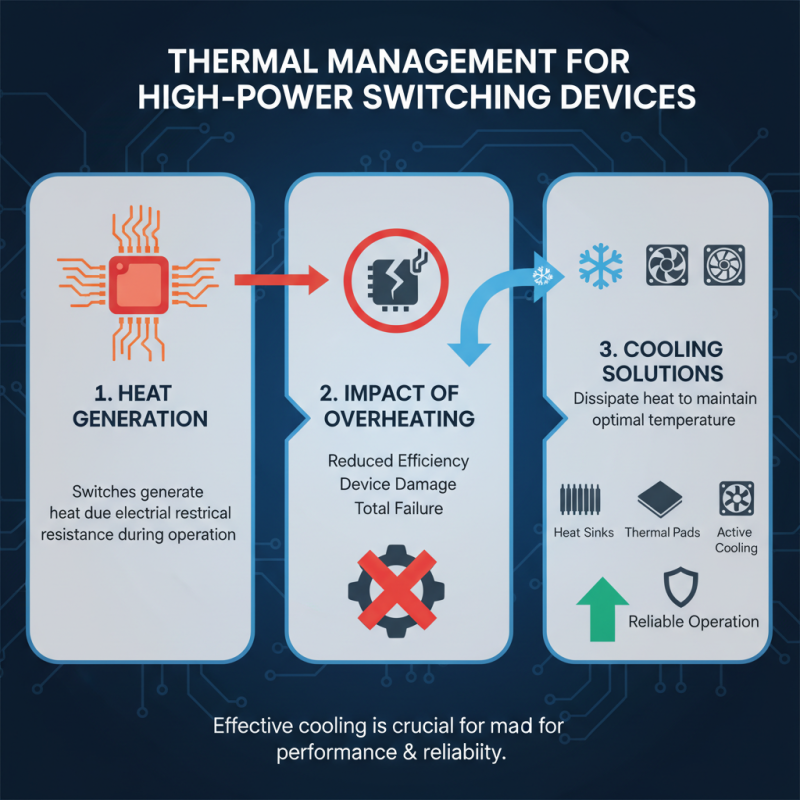
Thermal management plays a critical role in the performance and reliability of high power switching devices. When high power switches are in operation, they generate significant amounts of heat due to the resistance encountered during their switching action. This heat must be effectively dissipated to maintain optimal operating temperatures. If the thermal management is inadequate, devices may experience overheating, leading to reduced efficiency, possible damage, or total failure over time. To ensure reliable operation, it's essential to incorporate effective cooling solutions, such as heat sinks, thermal pads, or active cooling systems, tailored to the specific thermal demands of the application.
Moreover, the choice of materials and packaging can influence thermal performance. For instance, high thermal conductivity materials can enhance heat dissipation, while proper layout design on printed circuit boards can facilitate efficient airflow and thermal transfer away from critical components. Proper thermal management not only safeguards the high power switching devices but also improves overall system performance and longevity. By prioritizing these considerations in the design phase, engineers can create more robust electronics projects that can withstand the rigors of high-power applications.
When selecting a high power switch for electronics projects, assessing reliability and lifespan is paramount. High power switches often operate under severe conditions, which can significantly impact their longevity and performance. According to industry reports, factors such as thermal management, electrical ratings, and material quality critically influence these parameters. For example, switches that can handle higher temperatures might reduce failure rates, with studies indicating that a mere 10°C increase in temperature can halve the lifespan of electronic components.
Moreover, understanding the cycling capabilities and durability of a switch is essential. Data from recent studies indicate that the expected operational lifespan of high power switches can vary dramatically, with some achieving over 10 million cycles in optimal environments, while others may fail after just a few hundred thousand. This variability highlights the importance of selecting switches with robust performance metrics under expected usage conditions. Additionally, environmental factors, including humidity and dust ingress, should not be underestimated as they can compromise the integrity of high power switches, leading to potential failure in critical applications. By leveraging detailed reliability assessments and lifespan predictions, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance the overall performance and reliability of their electronics projects.
